Industrial Engineers Utilizing 3D Printing
11 May, 2020 | Industrial Manufacturing, Engineer, Industrial Engineering, 3D Printing
What is 3D printing?
3D printing allows users to build an object by printing material layer by layer until a three-dimensional object is formed. A computer-aided design (CAD) drawing or 3D model is used for the plans, and the objects are created from various materials including polymers, plastics, and metals using special printers. This technology isn’t new, the concept for it was ideated in the 1970s! But today, 3D printing is scaling up in a big way, and the 3D printing industry is estimated to reach $17 billion this year. The term Additive Manufacturing (AM) is often used to describe an industrialized version of the 3D printing process.
3D printing changes the work of industrial engineers
One of the great advantages of 3D printing is that it is fast – rapid prototypes were one of the first use cases of these devices, and that is remains one of the primary use cases. However, industrial engineers are pushing the limits of these devices and have moved far beyond the rapid prototype use case. Because these devices allow for greater flexibility and a lower cost of prototyping, companies around the globe are using the technology. Some benefits of 3D printing /AM include:
- Rapid prototyping
- Reduced waste
- Optimization of designs early
- Improved functionality
- Reduced costs
- Speeds up production
- Unlimited possibilities
- Accelerated time-to-market
- Ability to customize parts
- Agile design and engineering
What innovative approaches are being used?
Today, printers around the globe are being used to provide much needed medical equipment to first-line responders. From masks and components to face shields, engineers the world over have fired up their printers to provided protective equipment in response to COVID-19. The innovations don’t stop there, though.
In the past, 3D printers were limited to being able to print with only one type of material. Recent innovations, however, have developed printers that can use multiple printing materials – expanding the range of viable objects that can be printed immensely. These days, engineers are printing everything from shoes to homes – and everything in between.
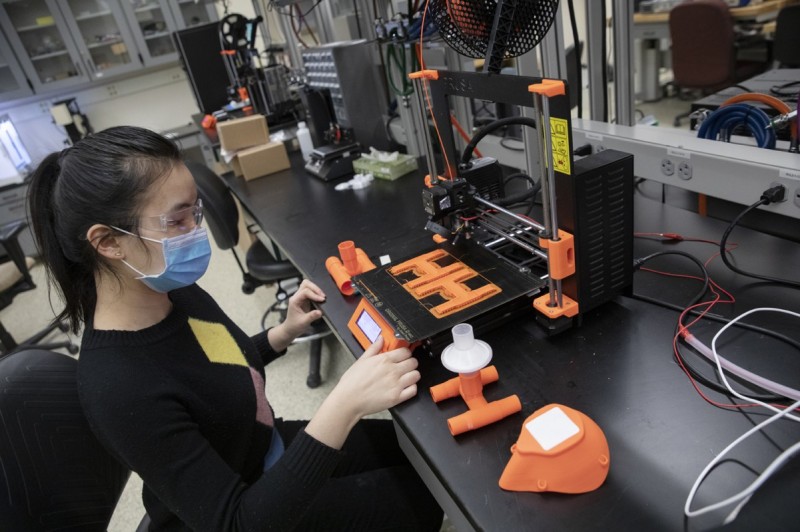

Shifts to industry
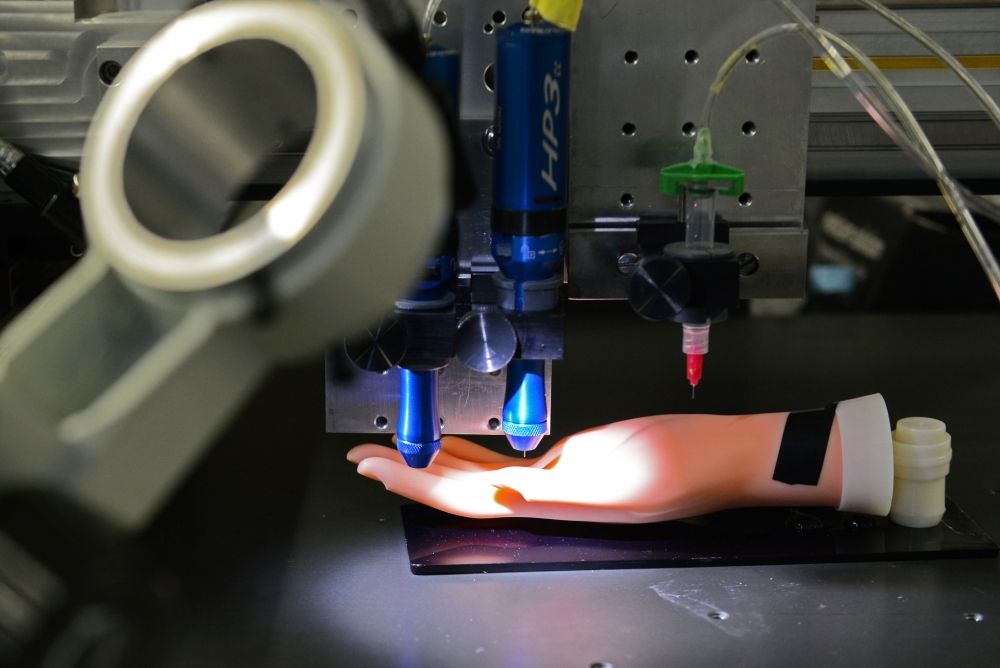
Industrial engineers in the aerospace industry are using 3D printers for low-volume parts, rocket parts, lightweight components, and for printing custom toolsets. The automotive industry is also using 3D printing for things like tooling and even replacement parts for vintage cars. The construction industry has seen the rise of 3D printing – enabling engineers to print walls, bridges, and even full homes! The healthcare field has seen massive use of the technology as well, with the printing of prosthetics, replica organs that can be used for practice, and even some testing of printing human organs to be used in organ transplants. The dental sector has seen brands creating 3D printed braces, bridges, and retainers. The energy industry has seen 3D printing on the rise as well, with some companies printing replacement parts. Recently, engineers at Purdue University announced they will be printing concrete wind turbines. Even industries you wouldn’t consider cutting edge are using 3D printing – including printing jewelry and even clothing – designer Zac Posen printed gowns for the Met Gala in 2019.
How will 3D printing affect industrial engineering in the future?
3D printing is the future of manufacturing – and the adoption across all industries will only continue to accelerate as the use cases go up and the costs continue to go down. The versatility of 3D printing will be a game-changer as well. More and more materials and methods are being developed that allow for printing in new and innovative ways. Engineers are improving design and quality while saving time and money by using 3D printing in their work. The design freedom offered by this medium allows for innovation – what the mind of the engineer can imagine, they can now create using 3D technology and modeling.










